Data security in healthcare protects patient information from cyber threats. It also guarantees compliance with regulations and maintains trust between providers and patients.
The security challenges faced by healthcare facilities are unique. Medical records contain sensitive data that must be kept accessible at all times for use in patient care.
This guide talks about security threats, regulatory requirements, and effective measures to secure data. Technical solutions, implementation strategies, and real-world examples are covered.
Data Security in Healthcare: Current Challenges
Healthcare organizations today handle vast amounts of sensitive patient data. They manage this data across multiple systems and platforms.
Medical records contain personal identifiers, financial information, and detailed health histories. This data attracts cybercriminals who seek valuable information.
Healthcare facilities face security challenges different from those of other industries. Patient care requires immediate data access, and this makes security measures more complex to implement.
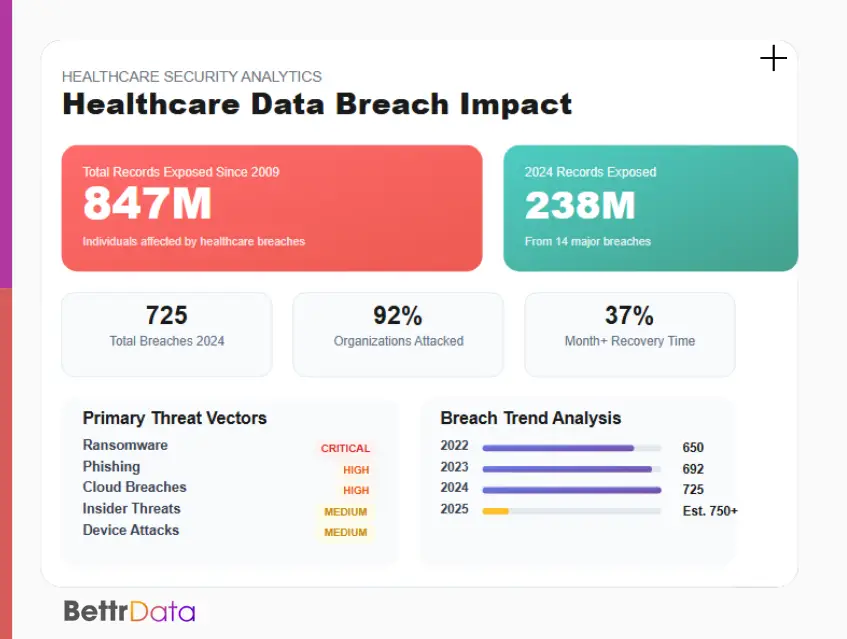
The healthcare sector experiences more data breaches than most industries. Patient records sell for high prices on illegal markets. This makes medical facilities prime targets for attacks that compromise data security in healthcare systems.
Effective healthcare data management requires robust security measures from the start.
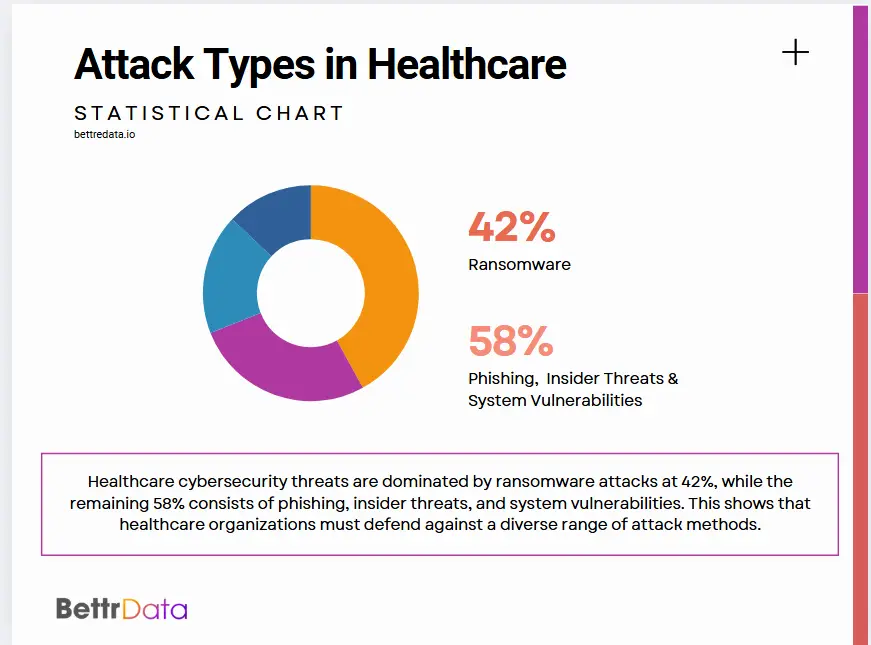
Major Healthcare Data Security Threats
Effective data security in healthcare requires understanding the primary threat vectors that target medical organizations. These attacks exploit both technical vulnerabilities and human factors.
| Threat Type | Attack Method | Target Systems | Impact Level |
| Ransomware | System encryption | Electronic health records | Critical |
| Phishing | Email deception | User credentials | High |
| Insider threats | Authorized access abuse | Patient databases | Medium-High |
| Device attacks | Unsecured endpoints | Medical devices | Medium |
| Cloud breaches | Weak access controls | Cloud storage | High |
External Cyber Attacks
Ransomware attacks encrypt healthcare systems and demand payment for restoration. These attacks disrupt patient care and expose sensitive data.
Phishing schemes trick employees into revealing login credentials. They also trick staff into downloading malicious software, and attackers often disguise themselves as trusted sources like IT departments or medical suppliers.
Healthcare has been one of the most targeted industries for cyberattacks in recent years, due to its valuable data and urgent operational demands.
Internal Security Risks
Staff members with legitimate system access can accidentally expose patient data. They can also intentionally expose this information and share passwords, leave systems unlocked, or mishandle sensitive information.
Third-party vendors and contractors create additional risk points. Healthcare organizations share patient data with billing companies, cloud providers, and specialized services.
These third parties may have weaker security controls that can compromise overall data security in healthcare networks.
HIPAA and Regulatory Compliance Requirements
Strong data security in healthcare starts with regulatory compliance. Healthcare organizations must meet specific federal and state requirements that govern patient information protection.
| Safeguard Type | Key Requirements | Implementation Focus |
| Administrative | Security officer designation | Staff training and policies |
| Physical | Facility access controls | Equipment and workspace protection |
| Technical | Access controls and encryption | System security and data protection |
| Organizational | Business associate agreements | Third-party vendor management |
HIPAA Security Rule Foundations
Healthcare organizations must protect electronic health information with proper safeguards – administrative, physical, and technical.
Administrative safeguards the security management process assigns security responsibilities, and ensures training of the workforce. Your organization should identify security officers, and conduct a risk assessment.
Physical safeguards protect computers, equipment, and facilities from unauthorized persons. It includes controls to enter the facility, appropriate utilization of workstations, and media controls for portable devices
Technical safeguards include access control, audit controls, integrity controls, and transmission security. Healthcare organizations should use user authentication and monitor data access to protect the integrity of information.

Additional Regulatory Requirements
Today, HIPAA requirements may be improved by state privacy laws. The HITECH Act extended HIPAA authority, penalties, and notification requirements for data breaches.
Healthcare organizations must continually subscribe to regulatory changes and modify security programs in line with them. The requirements of compliance continue to be altered as times change and with the introduction of new threats.
Essential Data Protection Strategies
Comprehensive data security in healthcare requires multiple protection layers that work together to safeguard patient information. These strategies address both preventive measures and incident response capabilities.
| Security Layer | Protection Method | Key Components |
| Access Control | User authentication | Multi-factor authentication, role-based access |
| Data Encryption | Information protection | At-rest and in-transit encryption |
| Network Security | Traffic monitoring | Firewalls, intrusion detection |
| Endpoint Security | Device protection | Antivirus, device encryption |
| Backup Systems | Data recovery | Regular backups, disaster recovery |
Access Control Implementation
Role-based access control ensures healthcare workers only access information necessary for their job functions. This principle of least privilege reduces unauthorized data exposure risks while maintaining operational efficiency.
Multi-factor authentication adds security layers by requiring multiple forms of identification before system access. This approach significantly reduces unauthorized access risks even when credentials are compromised.
Regular access reviews help organizations identify and remove unnecessary permissions. When employees change roles or leave the organization, their access rights must be updated or revoked promptly.
Data Encryption Standards
Healthcare organizations must encrypt patient information both at rest and in transit. Strong encryption standards protect data even if systems are compromised or information is intercepted during transmission.
Encryption key management requires careful planning and implementation. Organizations must securely store encryption keys and establish procedures for key rotation and recovery.
Database encryption protects stored patient records from unauthorized access. File-level encryption provides additional protection for sensitive documents and communications.

Technology Solutions for Healthcare Security
Modern data security in healthcare relies on advanced technology solutions that can detect, prevent, and respond to cyber threats. These tools provide automated protection and continuous monitoring capabilities.
| Solution Category | Primary Function | Key Benefits |
| Threat Detection | Attack identification | Real-time monitoring, behavioral analysis |
| Data Loss Prevention | Information control | Content monitoring, policy enforcement |
| Endpoint Protection | Device security | Antivirus, application control |
| Network Monitoring | Traffic analysis | Intrusion detection, anomaly identification |
| Security Analytics | Incident analysis | Pattern recognition, threat intelligence |
Advanced Threat Detection
Artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies help healthcare organizations identify security threats more effectively than traditional methods. Advanced healthcare data analytics can reveal suspicious patterns that human analysts might miss.
Behavioral analytics establishes baselines for normal user activity and alerts security teams when individuals exhibit unusual access patterns. This approach identifies both external attackers and internal threats.
Real-time monitoring provides continuous oversight of healthcare networks and systems. Automated response capabilities can isolate compromised systems while security professionals investigate incidents.
Data Loss Prevention Tools
Data loss prevention systems monitor and control sensitive information movement within healthcare networks. These tools prevent unauthorized copying, printing, or transmission of patient data while allowing legitimate business activities.
Email security solutions protect against phishing attacks and prevent accidental data exposure through email communications. These systems encrypt sensitive communications and filter malicious messages.
Endpoint protection secures individual devices that access healthcare networks. These solutions provide antivirus protection, application control, and device encryption to prevent data exposure through compromised endpoints.
Real-World Implementation Cases
Case Study 1: Regional Medical Center
A 400-bed regional medical center needed to modernize its data security infrastructure due to increased cybersecurity threats. The organization faced vulnerabilities in legacy systems, insufficient access controls, and inadequate employee training.
| Implementation Phase | Action Taken | Result Achieved |
| Risk Assessment | Conducted a comprehensive security evaluation | Identified critical vulnerabilities |
| Network Security | Implemented network segmentation | 75% reduction in security incidents |
| Threat Detection | Deployed advanced monitoring systems | Successfully prevented three ransomware attacks |
| Operations Center | Established security operations capabilities | Faster incident detection and response |
| Staff Training | Created comprehensive employee programs | Identified insider threats before data exposure |
| Patient Care | Maintained service quality during upgrade | Stable patient satisfaction scores throughout the process |
Case Study 2: Multi-Site Healthcare Network
A healthcare network operating 15 facilities across three states needed to standardize data security practices. The organization required consistent protection across all locations while maintaining effective data security in healthcare operations. The organization faced challenges coordinating security policies and managing diverse technology platforms.
| Strategy Component | Implementation Method | Delivered Outcome |
| Security Management | Implemented centralized management tools | 60% reduction in security incidents across the network |
| Incident Response | Established standardized procedures | Faster threat detection and response times |
| Threat Intelligence | Created shared intelligence capabilities | Enhanced coordination between facilities |
| Training Programs | Developed a unified education system | Improved employee security awareness through standardized training |

Implementation Best Practices
| Implementation Phase | Duration | Key Activities | Success Factors |
| Assessment | 2-3 months | Risk analysis, gap identification | Executive support, thorough documentation |
| Planning | 1-2 months | Strategy development, resource allocation | Clear objectives, realistic timelines |
| Deployment | 6-12 months | Technology implementation, training | A phased approach, minimal care disruption |
| Optimization | Ongoing | Monitoring, continuous improvement | Regular reviews, threat adaptation |
Executive Leadership Support
Healthcare administrators must champion security initiatives and allocate adequate resources for comprehensive protection programs. Leadership support ensures organizational commitment to data security goals.
Security programs require ongoing investment in technology, training, and personnel. Executive teams must understand that data security represents a critical business investment rather than simply a compliance requirement.
Clear accountability structures help ensure security responsibilities are properly assigned and monitored throughout the organization.
Employee Training Programs
Comprehensive training programs should address specific roles and responsibilities within healthcare organizations. Regular security awareness updates help staff recognize and respond appropriately to emerging threats.
Training content must balance security requirements with patient care responsibilities. Healthcare workers need to understand how security measures support rather than hinder their primary mission of patient treatment.
Simulation exercises and testing help reinforce training concepts and identify areas where additional education may be needed.
Measuring Security Program Success
| Metric Category | Key Indicators | Measurement Frequency |
| Incident Response | Detection time, resolution time | Monthly |
| Compliance | Audit results, policy adherence | Quarterly |
| Training | Completion rates, test scores | Quarterly |
| Technology | System uptime, false positives | Monthly |
| Risk Management | Vulnerability counts, threat levels | Monthly |
Performance Indicators
Healthcare organizations should establish metrics that demonstrate security program effectiveness. Regular measurement helps identify areas for improvement and validates security investments.
Incident response times indicate how quickly organizations can detect and respond to security threats. Faster response times typically result in reduced impact from security incidents.
Employee training completion rates show organizational commitment to security awareness. High completion rates correlate with better security practices throughout the organization.
Continuous Improvement
Regular security assessments help organizations identify weaknesses before they can be exploited. External security evaluations provide independent validation of security controls.
Threat landscape changes require adaptive security strategies. Organizations must regularly update their security programs to address new attack methods and vulnerabilities.
Technology refresh cycles ensure security tools remain effective against current threats. Outdated security systems may not provide adequate protection against modern attack techniques.
Future Trends and Considerations
Healthcare data security continues to evolve as new technologies and threats emerge. Cloud adoption will require organizations to develop expertise in cloud security management and vendor oversight.
Patient data rights and privacy expectations will likely expand as consumers become more aware of data collection and use practices. Healthcare organizations must prepare for evolving patient expectations and potential new regulatory requirements.
For organizations seeking to streamline data security operations and maintain strong protection, BettrData’s AI-powered platform offers automated data workflow management that reduces operational costs and increases security standards.
Strategic Next Steps
Start with your leadership team. Get executives on board and secure a budget for security initiatives. Without top-level support, security programs fail.
Build your foundation with a thorough risk assessment. This shows you exactly where your vulnerabilities are. Skip this step, and you waste money on the wrong solutions.
Roll-out technology changes slowly. Patient care comes first, so test everything before full deployment. Train your staff properly on new systems before going live.
If you do data mining in healthcare, build security into the process from day one. Don’t treat it as an afterthought that slows you down.

What You Need to Know to Secure Healthcare Data
Healthcare data security is complex but manageable. You need technical tools, clear policies, and physical safeguards working together. Balance is key – too much security blocks patient care, and too little invites disaster.
The cost of getting hacked far exceeds the cost of prevention. One breach can destroy years of reputation-building. Smart organizations invest early and avoid the pain later.
Start with a solid plan. Get your executives committed. Know your risks. Build systematically. Stay flexible as threats change. Success takes time but pays off big.
If you want to protect sensitive health data, reduce security risks, and stay compliant without slowing down patient care or draining engineering resources, BettrData can help.
By automating 91% of pipeline processes, BettrData’s solutions enable healthcare organizations to securely scale, onboard faster, conform to requirements promptly, and minimize operational expenditures. Secure your healthcare data with speed — contact us here to get started with BettrData.


